Since the discovery of SARS-CoV-2 in China on January 9, 2020, we have been inundated with more or less verified information on the pandemic. It is useful to take stock of the scientific knowledge on the subject, with Jean-Marc Sabatier*.
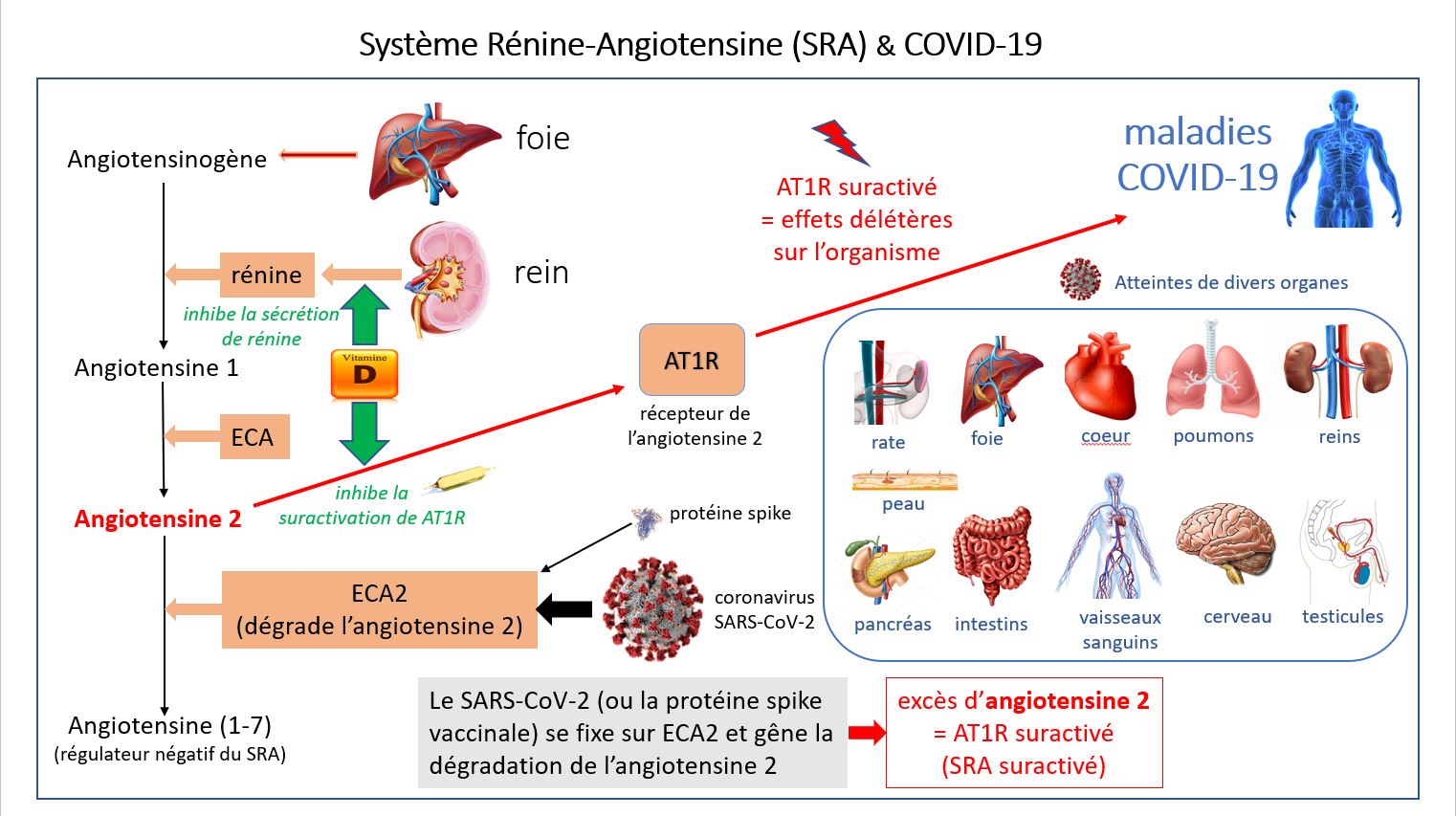
The AT1R receptor has vasoconstrictor (hypertensive), pro-inflammatory (cytokine storm), pro-thrombotic, pro-fibrosing, pro-oxidative (causes oxidative stress), pro-angiogenic, hypertrophying organs (heart, lungs, etc.), inhibiting the production of nitric oxide (NO) affecting the immune and nervous systems…
The over-activated AT1R receptor (= RAS dysfunction) is thus the real culprit in Covid-19 diseases.
- SARS-CoV-2 virus induces dysfunction (over-activation) of the renin-angiotensin system.
- The dysfunction (over-activation) of the renin-angiotensin system is responsible for Covid-19 diseases.
- The vaccine spike protein circulates freely in the blood.
- The spike protein is responsible for the deleterious effects of SARS-CoV-2.
- The spike protein binds to the ACE2 (angiotensin converting enzyme 2) receptor of the target cells.
- Vitamin D inhibits over-activation (dysfunction) of the renin-angiotensin system.
- Vitamin D prevents progression to the severe forms of Covid-19.
- Vitamin D has beneficial effects on Covid-19 and the immune system.
Vaccinated and infected
- People infected with SARS-CoV-2 can transmit the virus.
- Children are less susceptible than adults to SARS-CoV-2 infection and their lethality to Covid-19 is almost zero.
- SARS-CoV-2 can be transmitted to other mammals (very rare cases), such as dogs, cats, lions, tigers, ferrets and mink.
- The SARS-CoV-2 virus is found in the stool of infected individuals.
- An oral-digestive route of infection for SARS-CoV-2 is likely (but not proven).
- Persons vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 may become infected with the virus and its variants.
- Persons vaccinated and then infected with SARS-CoV-2 can transmit the virus.
- The over-activated AT1R receptor (of the renin-angiotensin system) is responsible for the pathologies of Covid-19.
- Vaccine efficacy is decreasing with the emergence of new variants of SARS-CoV-2.
- Vaccination (partially) protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection and Covid-19 disease.
- Natural immunity acquired after SARS-CoV-2 infection is greater than immunity acquired after vaccination.
- Herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2 cannot be achieved with the emergence of transmissible variants in vaccinated individuals.
Essential barrier measures
- The Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is more infectious, but less lethal than the original strain of the virus.
- SARS-CoV-2 disrupts innate immunity.
- SARS-CoV-2 affects renal, pulmonary and cardiovascular function.
- SARS-CoV-2 disrupts the intestinal microbiota.
- Existence of genetic susceptibility factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection and Covid-19 diseases.
- The effectiveness of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 depends on the vitamin D status of the vaccinee.
- Barrier measures (hand washing, distancing, wearing a mask) protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
- Diet may affect susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 and Covid-19.
- SARS-CoV-2 vaccines can (rarely) induce Covid-19 disease.
Glossary
SARS-CoV-2
During viral infection, SARS-CoV-2 over-activates the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) by binding to the ACE2 receptor, which has an angiotensin 2 degradation function. The binding of SARS-CoV-2 to the ACE2 receptor thus prevents the normal degradation of angiotensin 2, the excess of which leads to an over-activation of its cellular receptor AT1R. The overactivated AT1R receptor is very deleterious to the human body (induction of cytokine storm, vasoconstriction, inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, angiogenesis, tissue hypertrophy, fall in nitric oxide NO related to immunity and memory processes, etc.) and seems to be at the origin of the progression to the severe, sometimes fatal, forms of Covid-19. This deleterious effect of AT1R on the human body results in the development of various pathologies similar to those described for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The genes coding for ACE2 and AT1R are located on chromosomes X and 3, respectively.
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS)
The RAS is a major hormonal/physiological system in mammals, present in the lungs, kidneys, intestines, heart, brain, spleen, pancreas, testes, blood vessels, as well as on “innate” immunity cells (circulating monocytes, macrophages, dendritic/antigen-presenting cells, natural killer (NK) cells, etc.). The RAS controls renal, pulmonary and cardiovascular functions, as well as “innate” immunity (which is the “immediate” non-specific immune response to pathogens) and the gut microbiota.
The gene encoding the AT1R receptor (of the RAS), which is highly deleterious to the human body when overactivated, is located on chromosome 3. It is notable that chromosome 3 contains a neanderthal haplotype (a set of “genetically linked” genes located on the same chromosome and transmitted together to the next generation) associated with severe forms of Covid-19. This haplotype is found at 16% in Europe, 65% in South Asia, and is almost non-existent in East Asia and Africa).
Vitamin D is a seco-steroid pro-hormone that acts on at least 291 genes, hence its involvement in many physiological processes: bone mineralization and calcification, innate (circulating monocytes, macrophages, dendritic/antigen-presenting cells, Natural Killer (NK) cells, etc.) and adaptive/acquired (B and T lymphocytes) immunity, proliferation and differentiation of certain cell types (including immune system cells), maintenance of physical barriers (effect on the immune system), and the development of the immune system. ) and adaptive/acquired immunity (B and T lymphocytes), proliferation and differentiation of certain cell types (including immune system cells), maintenance of physical barriers (effect on intercellular junctions), and regulation of RAS. In particular, vitamin D prevents/mitigates the cytokine storm that is very harmful to the human body (excessive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-1-beta, interferon-gamma, etc.), which is at the origin of the evolution towards the severe forms of Covid-19. At the same time, vitamin D enhances the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines via adaptive/acquired immunity to inhibit acute systemic hyperinflammation.
Another action of vitamin D on immunity is to directly induce the production of anti-microbial molecules active on viruses (cathelicidin and defensins).
Thus, vitamin D allows the optimal functioning of the immune system necessary for effective vaccination, and induces the production of molecules with antiviral properties allowing the host to prevent or treat possible infection with SARS-CoV-2 and its variants.
Self molecules
These are molecules belonging to the host and which the immune system should not attack.
Non-self” molecules
These are molecules that are “foreign” to the host, generally from pathogens, and which the immune system must attack.)
Vaccine “spike” protein
This is actually the (modified) spike of SARS-CoV-2; it is a trimer of the modified S protein, from which the fusogenic domain allowing the penetration of the virus into cells has been removed.

*Jean-Marc Sabatier, Director of Research at the CNRS and Doctor in Cell Biology and Microbiology, affiliated with the Institute of NeuroPhysiopathology (INP), at the University of Aix-Marseille. Editor-in-Chief of the international scientific journals: “Coronaviruses” and “Infectious Disorders – Drug Targets”.

